Mobility Parts: Harmony of lightness and strength
Advancing mobility competitiveness with the latest lightweight technologies
Hyundai Steel contributes to improving both fuel efficiency and safety in automobiles by producing ultra-high-strength lightweight components through advanced methods such as hot stamping, TWB, hydro-forming, and bipolar plates. In particular, we precisely manufacture complex-shaped components, which are applied to various automotive parts, achieving reduced emissions and improved fuel efficiency through lightweighting technology. Hyundai Steel continues to innovate and develop technology to meet the changing demands of the automotive industry, strengthening its competitiveness in eco-friendly vehicles and next-generation mobility components for global automobile manufacturers.
-

- 4th in the world
- Hot stamping component production capability
-

- World’s largest scale factory
- Production of hot stamping parts on 21 Lines Single factory owned
-

- Ultra-high strength parts
- World’s first mass production of 1.8 GPa grade hot stamping ultra-high strength steel
-

- World’s first bipolar plate
- World’s first mass production of key components for hydrogen fuel cells
Hot Stamping
Hyundai Steel’s hot stamping process involves heating 60K grade steel sheets to over 900°C, and then forming and rapidly cooling them within a mold to produce 150K grade ultra-high-strength parts. This method increases strength by more than three times compared to regular stamped steel sheets, while simultaneously allowing for the molding of complex-shaped components. Applied to various components such as roof rails, outer lowers and instrument panel cross members, it enables both lightweighting of the vehicle body and improved crash safety, significantly improving vehicle performance and safety.
Key features
- Lightweighting
- Ultra-high strength
100-180K -
Top supplier
for Hyundai
Motor Group
Advantages
- Approximately three times stronger than existing methods
- Vehicle lightweighting and enhanced passenger safety
- Overcoming shaping
technology limitations of ultra-
high strength steel - Improved productivity and reduced investment costs
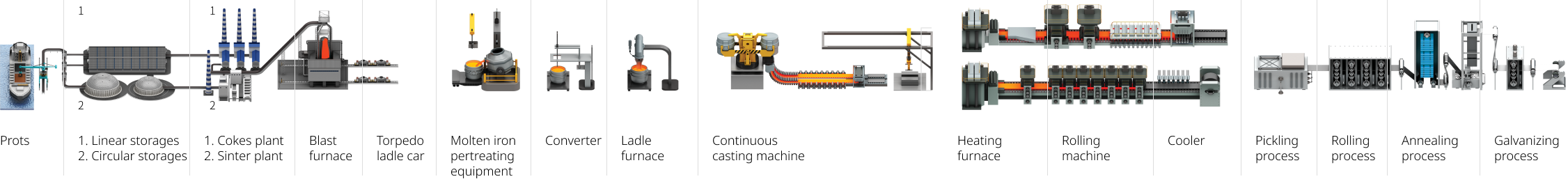
Application and key components

Center pillar

Rear member
Process flow
-
- Material heating process
- Prior to press forming, the steel sheet is heated to 930-950°C for 5 minutes during the heating/softening process
-
- Press forming process
- Simultaneously forming and rapidly cooling to achieve the desired shape
-
- Laser cutting process
- Cutting unnecessary parts to fit the shape of the product, completing the final product
TWB (Tailor Welded Blank)
TWB is a process that combines plates of different thicknesses and materials into a single blank through laser welding. This process maximizes lightweighting and rigidity, allowing for the precise manufacturing of complex-shaped components. TWB is primarily applied in automotive body structures and is a key technology that maximizes customer business value by improving fuel efficiency and enhancing safety.
Key features
- Lightweighting
-
Reduction of
component
count -
Collision
performance (dual material welding)
Advantages
- Optimal placement with
required strength and
thickness for each area -
Weight reduction and
strength improvement -
Increased fuel efficiency
through lightweighting - Cost reduction
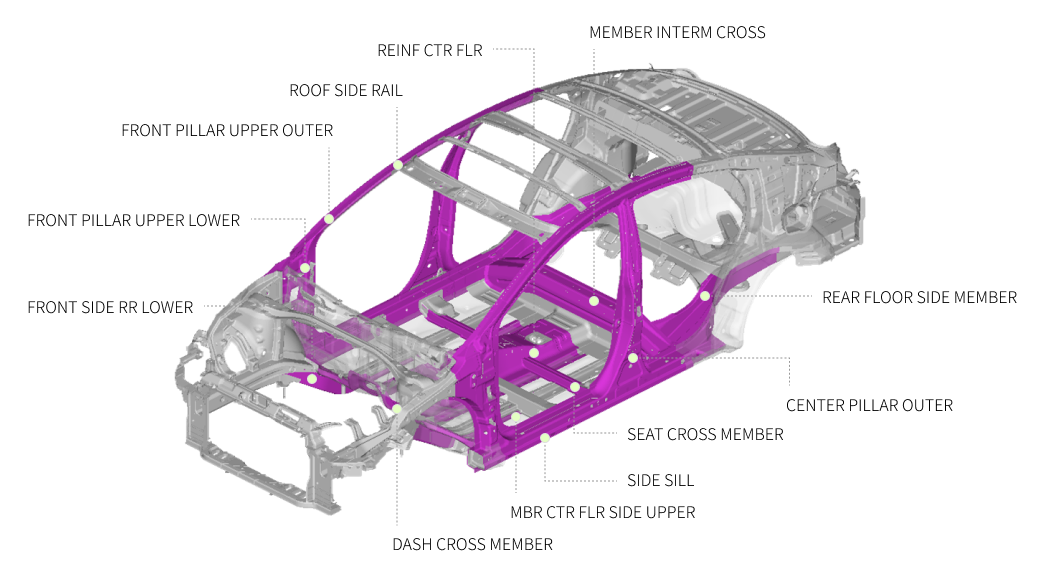
Application and key components


Roof side outer
(TWB+Hot Stamping)


Center pillar
(TWB+Hot Stamping)
Process flow
-
- Material alignment
- Aligning the cut coils on a jig for laser welding into the desired shape
-
- Laser welding
- Welding is performed using a high-power laser on the precisely aligned areas
-
- Quality inspection
- Weld quality inspection is conducted simultaneously with welding using automated inspection equipment
Hydro-Forming
Hydro-forming is a method that involves pre-forming a steel tube and then applying high hydraulic pressure to shape it into the desired form. This process replaces existing welded components, reducing the number of parts and contributing to lightweighting, and is primarily used in automotive parts such as complex-shaped trailing arms and rear side members. It simultaneously achieves strength and weight reduction, improves product quality, and enhances NVH (Noise, Vibration, Harshness) performance. This contributes to improved fuel efficiency and enhanced safety, establishing itself as an essential method for the design and production of high-performance vehicles.
Key features
- Lightweighting
-
Collision
performance -
Quality
improvement (noise and vibration)
Advantages
-
Improved durability and
10-20% weight reduction - Cost reduction
- Excellent dimensional quality
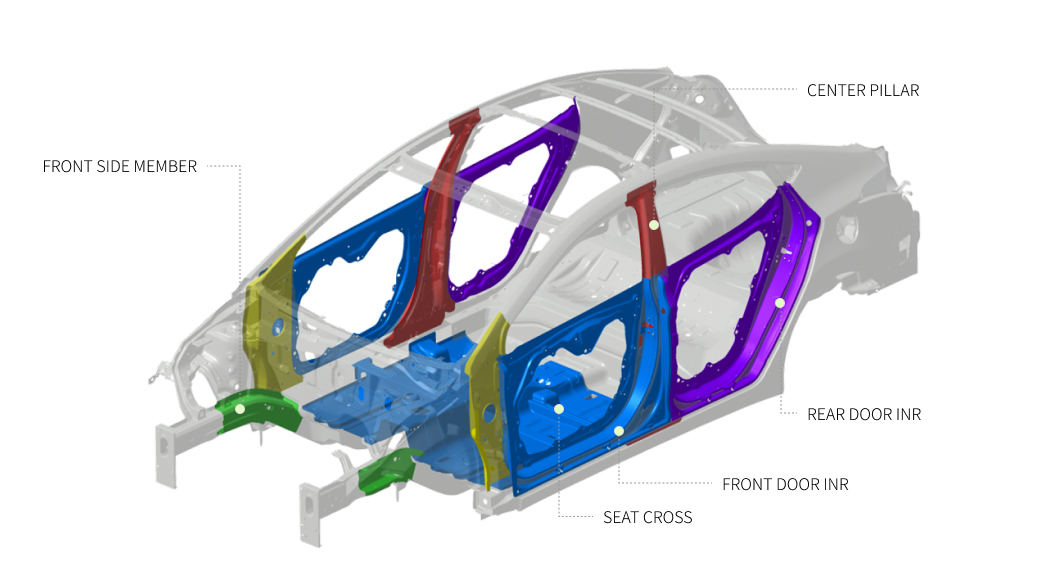
Excellent dimensional quality

Rear side member

Trailing arm
Process flow
-
- Bending process
- The process of bending a steel tube to the desired angle
-
- Pre-forming process
- Pre-forming is performed to ensure proper fit into the hydro-forming mold
-
- Hydro-forming process
- Water fills the interior through both ends of the pre-formed steel tube, and product shaping occurs at a maximum hydraulic pressure of 2000 bar
-
- Laser cutting process
- The final product is completed using a laser cutting machine
Metal Bipolar Plates(Bipolar plates)
Bipolar plates are key components that separate hydrogen and oxygen in hydrogen fuel cells to generate electrical energy, while being environmentally friendly products that reduce noise and vibration. The process involves steps such as Au-nano coating, heat treatment, spot welding, and automated inspection, utilizing technologies that maximize durability and quality. This product is used in hydrogen vehicles and energy storage systems, playing a crucial role in lightweighting and performance enhancement. Hyundai Steel provides significant value in the eco-friendly mobility market through these bipolar plates, strengthening its competitiveness in future automotive components.
Key features
- Hydrogen
business - Eco-friendly
- Quality improvement (noise and vibration)
Application areas
- Application areas
- Residential use
- Water electrolysis
- Military/Drone
Key components

Anode

Cathode
Process flow
-
- Coating
- Au-nano coating on the formed separator plates.
-
- Heat treatment
- Improved adhesion and corrosion resistance
-
- Joining
- Joining of the anode and cathode of the bipolar plate
-
- Inspection
- Automated inspection for dimensional accuracy, airtightness, welding quality, and appearance defects
Manufacturing process
Hynndai Steel's intergrated steelworks manufacture hot-rolled and cold-rolled coils, heavy plates, pipes, and lightweight automotive parts out of iron ore and coal. By melting lumps of raw materials, molten metal is generated in blast furnaces, after which it is purified in the steelmaking process and then goes on to the continuous casting process to make slabs that can also be hardened half-finished products. Those of slabs are thoroughly rolled at a high temperature (above 1,100℃) in order to make hot-rolled coils. After that, the cold-rolled coils are made by rolling the HRC (hot-rolled coils) at room temperature to process for final usage, which is mainly for lightweight automotive parts.
Hyundai Steel’s electric arc furnace uses steel scrap to manufacture sections, reinforcing bars, and railway rails that are used for buildings, bridges and railways. After melting the steel scrap to make molten metal, it is then smelted to eliminate impurities before proceeding to the continuous casting process to manufacture halffinished products, such as blooms and billets. These half-finished products can be rolled by reheating to increase their size as finished products, such as sections and reinforcing bars, in various sizes and thickness.