Environment: Managing the Environment for the Future
Hyundai Steel responds to climate change based on integrated environmental management and continuously improves its environmental management system
Integrated environmental management
Hyundai Steel is planning to invest 680 billion won over five years from 2021 to 2025 for environmental improvement and greenhouse gas reduction. Including this investment, we have invested approximately 1.2 trillion won in environmental improvement over 10 years (2016-2020: 510 billion won investment) to establish an advanced environmental system and proactively respond to environmental issues. The company plans to install Coke Dry Quenching (CDQ) and coke desulfurization and denitrification facilities, as well as make investments to improve the quality of COG from the Hwaseong Phase 1 and Phase 2 plants.
An investment of approximately 1.2 trillion KRW over 10 years
Implementing systematic environmental management processes for proactive risk response
-

Climate change
response -

Energy
management -
Pollutant
management -
Resource recovery
of by-products
Integrated environmental management policy
- Management activity risk analysis
-
- Proactive response to government policies and regulations
- Information gathering on environmental and energy issues
- Prediction, evaluation, and response to environmental impacts
- Efficient use of energy and resources
-
- Management of fuel, raw materials, equipment, and energy
- Optimization of process inputs and reduction of greenhouse gases
- Water resource reduction and risk management
- Minimizing emissions and pollution
-
- Measurement of pollutants and prevention of dispersion
- Optimal operation and monitoring of prevention facilities
- Resource recovery and value addition of by-products
- Fulfilling ethical and social responsibilities
-
- Enhancing brand value through community coexistence and CSR activities
- Utilization of alternative resources and energy
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
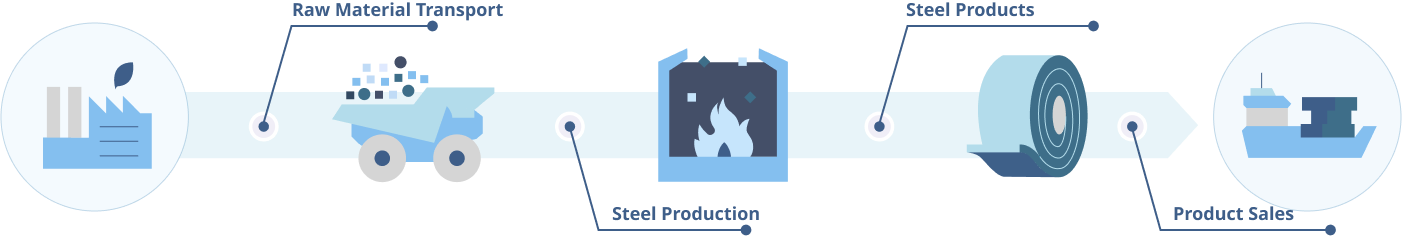
Hyundai Steel establishes and operates a carbon footprint assessment system through Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). The scope of the LCA for steel products includes raw material extraction, raw material transportation, product production, and product shipment. In 2020, we established an internal system to calculate the carbon footprint of products (CFP) independently, and we plan to receive third-party verification or certification to ensure the consistency and reliability of the data.
LCA scope for steel products
- Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) certification
- Since 2019, our company has obtained domestic and international EPD (Environmental Product Declaration) certifications in order to respond to customer demands for environmental information on our products. We have been continuously maintaining these certifications and renewing their validity to ensure compliance. This demonstrates objectively that our products meet the environmental standards required by our customers and reflects our commitment to providing the relevant information.
Energy management

Hyundai Steel participated in the government-led Korean Energy Efficiency Innovation Partnership ‘KEEP30’ in October 2022, and aims to achieve an energy reduction rate of 5% from 2023 to 2027 by implementing various energy-saving activities. In addition, through the ISO 50001 (Energy Management System) certification, we are committed to improving energy efficiency and usage throughout the entire process, from energy planning to implementation of improvements.
- Optimization of automatic control operation for hot blast stoves
- Hyundai Steel has implemented hot blast stove automation to improve the efficiency of the hot blast stoves, which are facilities with high fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in the blast furnace process. In addition, technology for optimizing dome temperature and flue gas temperature to create thermal conditions that minimize heat loss has been applied to all blast furnaces in 2023. Through this, the company has reduced approximately 235,000 Gcal of by-product gas annually.
- Development of a virtual sensor for predicting coke oven temperature
- Hyundai Steel has developed a virtual sensor1) for predicting coke oven temperature using AI to improve the efficiency of the coke ovens, aiming to enhance the accuracy of the target temperature within the furnace. In 2023, the development of the virtual sensor for the No. 3 coke plant was completed and applied to the No. 3 coke plant, and similar implementations are planned for the No. 1 and No. 2 coke plants as well. Virtual sensors: Predict secondary properties required for operations by analyzing patterns between operational data and experimental results using machine learning algorithms.
Pollutant management

- Air pollution management
- Hyundai Steel is strengthening its air quality management system by enhancing internal management standards for major air pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and odors, as well as expanding improvement investments. Furthermore, we are actively participating in external initiative activities such as the Coexistence Environmental Forum, carbon neutrality implementation agreements, and fine dust reduction campaigns, demonstrating our commitment to both internal and external efforts.
- Investment in NOx reduction facilities
- The company plans to sequentially introduce a total of 18 Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems and 5 low-NOx burner systems in the heating furnaces and annealing furnaces located in Incheon, Pohang, Dangjin, and Suncheon by 2025. In addition, through a national project, we have completed the research and development of a “low-temperature catalyst” that exhibits excellent nitrogen oxide removal performance at low exhaust gas temperatures, and it was applied to one heating furnace at the Dangjin plant in December 2023.
- Odor management response
- In 2023, the company invested approximately 4 billion won to improve major odor sources at the Dangjin Steelworks and has completed the expansion of odor control facilities and other improvement works. The odor control facilities are installed and operated under the condition of guaranteeing a stricter air dilution sensory method standard of below 300 times, which is more stringent than the regulatory standard of below 500 times in the odor prevention regulations.
- Chemical substance management
- Since 2015, Hyundai Steel has been operating a chemical management system to comply with relevant regulations, including the Chemical Substances Control Act, the Act on the Registration and Evaluation of Chemical Substances, and the Occupational Safety and Health Act. All materials classified as chemicals undergo a two-step verification of their composition and harmfulness before being received at the facility, and only those deemed suitable can be accepted. In addition, we update and manage the material safety data sheets for all chemicals by registering them in the system.
Resource recovery of by-products
Development of rapid-hardening cement from reductive slag
Hyundai Steel has developed rapid-setting cement using reducing slag, which allows for quick strength gain after curing, thereby expanding the scope of utilization for by-product recycling products. This product is a cement-free material mixed with 70-80% reducing slag and 20-30% gypsum, characterized by its ability to achieve high strength in a short time after curing.

Hyundai Steel reductive slag
Ettringite compounds
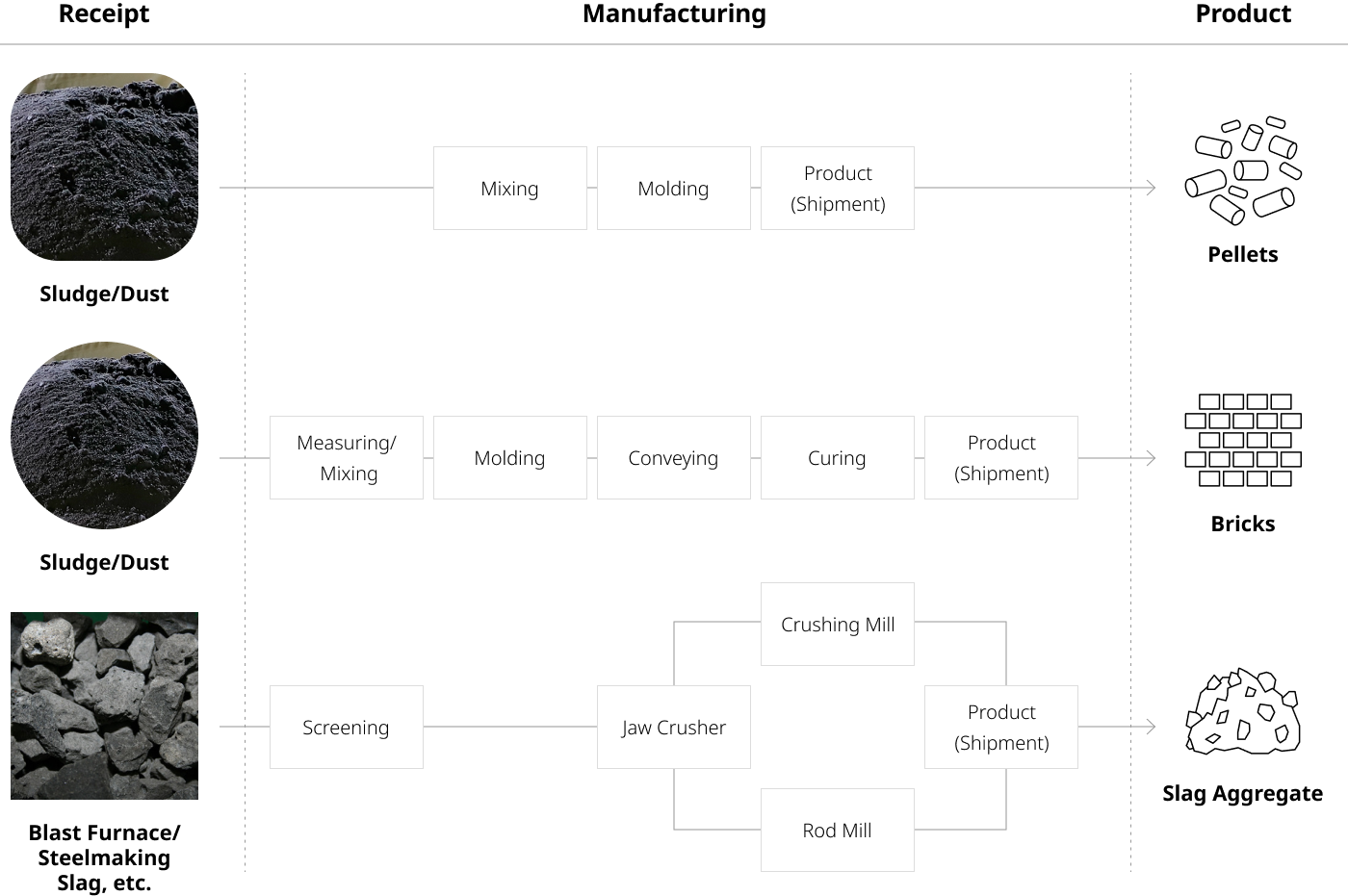
Operation of by-product resource recovery self-treatment facilities
Hyundai Steel operates self-treatment facilities to directly recycle various by-products, aiming to reduce facility waste generation and increase the recycling rate. We produce pellets and bricks using sludge and dust, and create products such as aggregate slag and hydraulic slag from slag. Slag produced during the manufacturing of products such as plates, hot-rolled, cold-rolled, and rebar is crushed and processed through pneumatic conveying equipment to be reborn as slag aggregate products. Slag products are recycled for various uses in construction materials.
Self-treatment facility operation process