Carbon Neutrality: Pathway to Green Steel
Hyundai Steel strives to become a steelmaker capable of sustainable growth by committing to carbon neutrality
Hyundai Steel’s Roadmap to Carbon Neutrality
In April 2023, Hyundai Steel announced its long-term goal to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, a target we are pursuing through phased technology upgrades and ongoing decarbonization efforts. In line with South Korea’s Nationally Determined Contribution plan, Hyundai Steel plans to reduce Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 12% from 2018 baseline levels by 2030. Residual emissions that are unavoidable by 2050 will be offset through carbon credit trading, carbon capture, utilization and storage(CCUS), blue carbon initiatives,
and forest creation efforts, to ultimately achieve net-zero emissions.
In 2024, we established our own “Scope 3 Calculation Internal Guideline” based on the GHG Protocol. We are currently operating a Scope 3 calculation system integrated with internal systems such as raw material and logistics, among others.
Carbon Emission Reduction Targets ( ~ 2050)
- 4,000
- 3,000
- 2,000
- 1,000
- 0
Hyundai Steel’s Carbon Neutrality Strategy
Our carbon reduction strategy follows a two-pronged approach: reducing the carbon footprint of our products and minimizing the emissions from our production process. We aim to support our customers’ journey towards carbon neutrality by providing them
low-emission1) products.
Simultaneously, we plan to work towards our own emissions reduction goals by actively exploring ways to lower the emissions of our production process.
Hyundai Steel will adopt the “Electric Arc Furnace – Blast Furnace Combined Process” in the short term to produce products with lower emissions compared to our conventional blast furnace products.2) In the long term, we aim to further reduce the carbon footprint of our products hydrogen-based iron-making and large-scale application of electric arc furnaces.3)
Short- to Long-term Transition Plans
[Short- to Mid-Term Phase 1]
EAF-BF Combined Process (Q1 2026 ~ )
In Phase 1, scrap iron and HBI are pre-melted in the electric arc furnace, and the molten steel is then combined with molten iron from the blast furnace in the basic oxygen furnace.
This process produces steel products with a carbon emission reduction of approximately 20%4) compared to conventional blast furnace products.
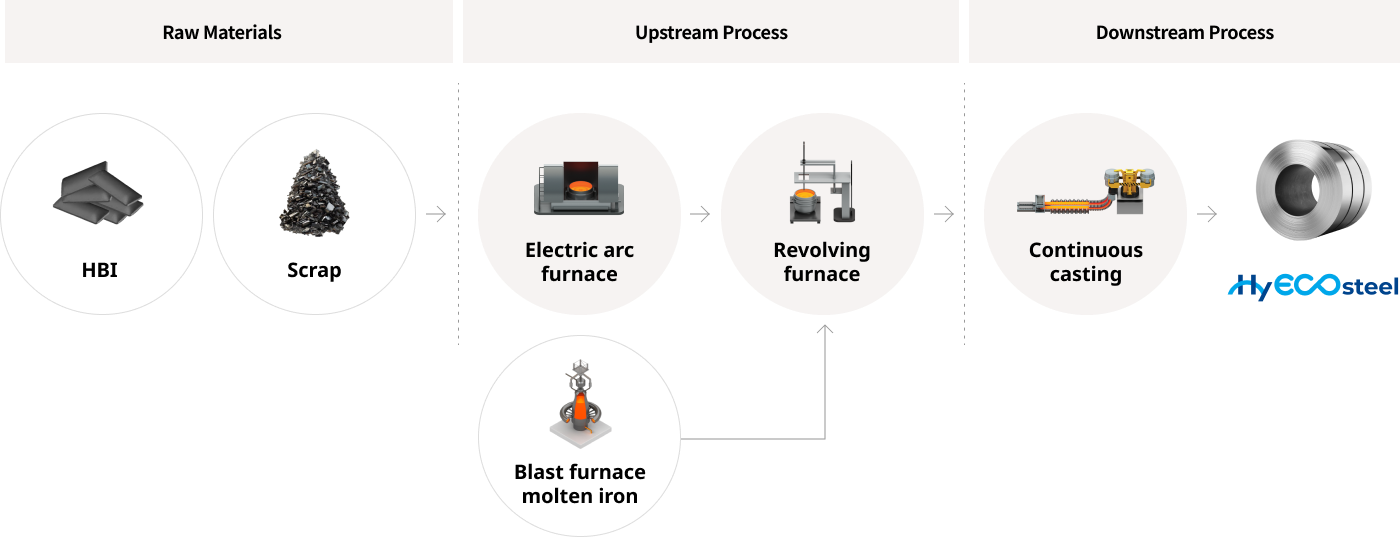

[Short- to Mid-Term Phase 2]
Hy-Arc method (Under R&D)
In Phase 2, molten iron from the blast furnace will go directly into the Hy-Arc, our large-scale, high speed electric arc furnace.
We expect that this process will allow us to produce 70% of our current automotive product portfolio, with products
that have a carbon emission reduction of approximately 40%* compared to Hyundai Steel’s conventional blast furnace products.
*40% reduction in carbon emissions refers to CO₂-equivalent (CO₂e) values, calculated internally based on a cradle-to-gate emissions in accordance with ISO 14044.
Hyundai Steel became the first in the world to successfully test-produce 1.0GPa high-strength steel using an electric arc furnace in 2022. This achievement demonstrated that high-quality steel can be produced through EAF. Building on this milestone, we will continue our R&D efforts to advance our Hy-Arc process.
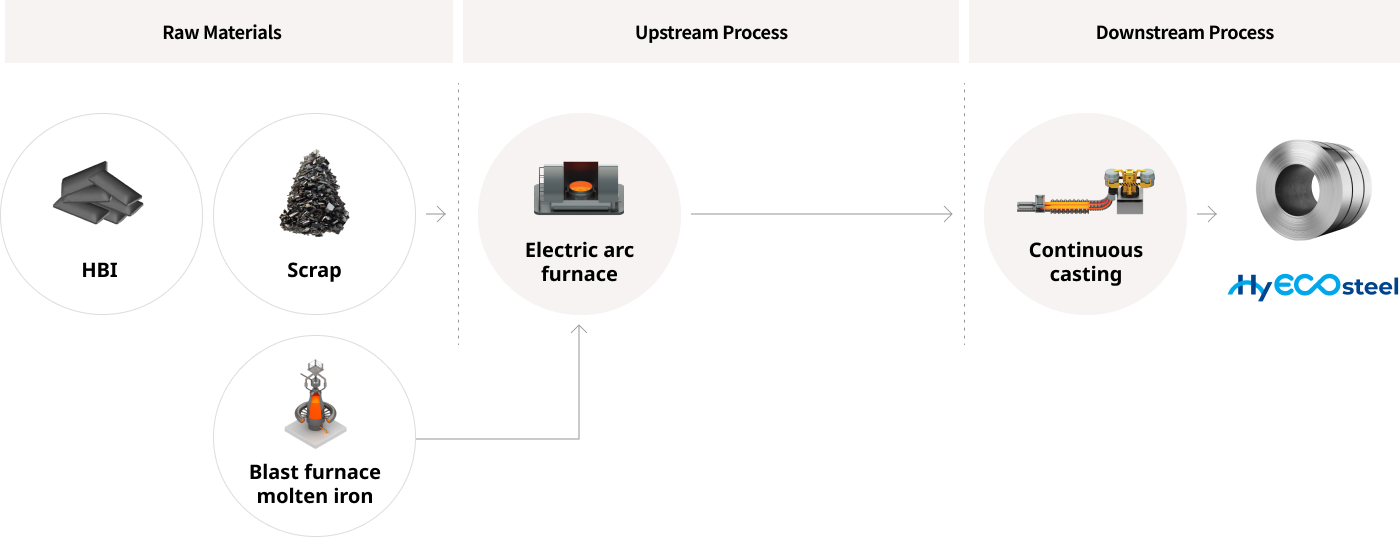

[Long Term]
Hydrogen-based Steelmaking (~2050)
In the long-term, Hyundai Steel plans to transition from traditional coal-based steelmaking to hydrogen-based steelmaking. Through this process, we aim to produce products with a reduction in carbon emissions of approximately 90%.
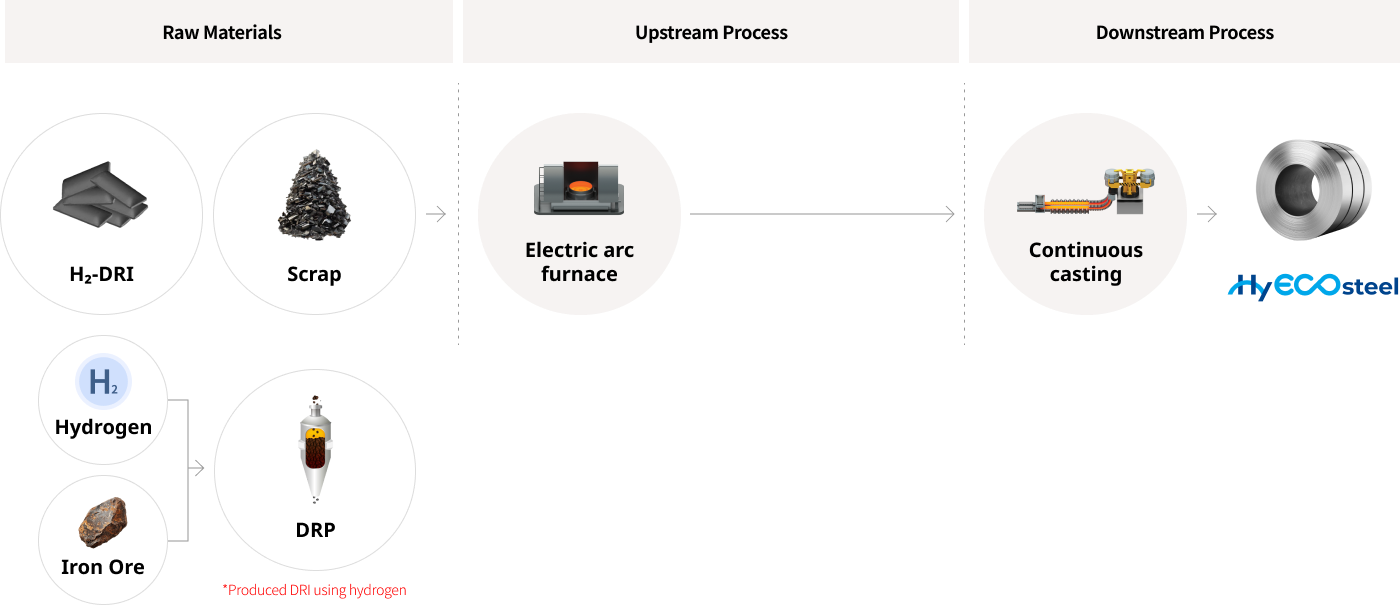

Process Emission Reduction
Hyundai Steel is committed to steadily lowing carbon emissions in its manufacturing process through various methods such as applying carbon reduction technologies in ironmaking and enhancing energy efficiency.
-
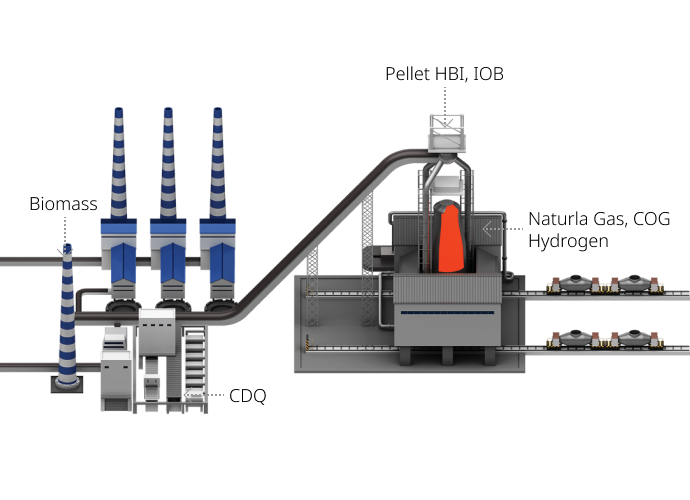
- Emission Reduction in the Ironmaking Process
- We have adopted strategies such as increasing low-emission fuels and raw materials, introducing CDQ facilities, and optimizing operations to reduce the carbon emissions in the ironmaking process.
-

- Improvement in Energy Efficiency
- We strive to optimize our manufacturing process to reduce carbon emissions by increasing self-generated power and enhancing energy efficiency.
HyECOsteel, Hyundai Steel’s low-emission steel brand
Hyundai Steel’s low-emission1) steel, “HyECOsteel” supports customers in their mission towards carbon neutrality.

Brand Name
“Hy” reflects Hyundai Steel’s long-term vision and proactive approach to adopting advanced steelmaking technologies, including hydrogen-based and hybrid processes, as they become commercially viable and mature.5) Within our brand context, "ECO" explicitly represents our long-term vision and strategic goal of transitioning towards sustainable steelmaking. This reflects our efforts to gradually reducing carbon emissions through measurable steps, recognizing that we are currently in a transitional phase. Hyundai Steel has a goal of gradually reducing its emissions, and detailed information on our carbon reduction targets can be found here.
Brand Design
The “Hy” was designed to resemble a bridge, while an infinity symbol is hidden within “ECO”.
The design collectively symbolizes Hyundai Steel’s commitment to bridging nature and humanity.
The infinity symbol further represents our philosophical ambition and continuous efforts towards sustainability.
※ The color of the logo is based on Hyundai Steel’s CI.
HyECOsteel is produced via the Electric Arc Furnace-Blast Furnace Combined Process and generates 20% less carbon emissions4) compared to our conventional blast furnace steel2). Our HyECOsteel products can meet the needs of customers in various sectors ranging from automotive, construction, shipbuilding, and whitegoods.

We plan to mass-produce HyECOsteel starting in 2026. HyECOsteel has lower carbon emissions while maintaining the same quality as our conventional blast furnace products. In the long term, we are exploring the possibility of offering low-emission products through our Phase 2 and long-term transition plans.
HyECOsteel
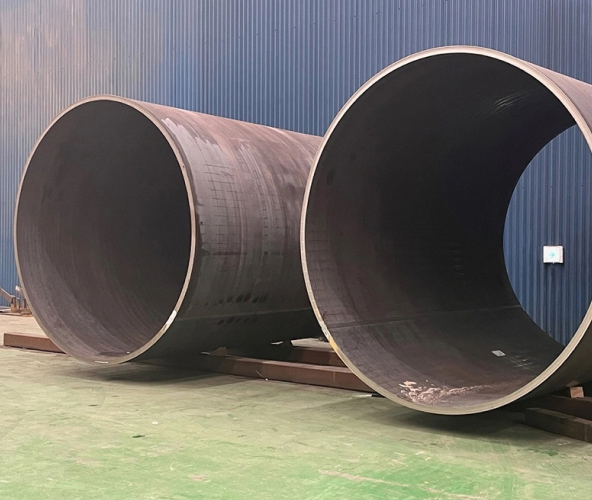

Electric Arc Furnace
Blast Furnace Combined Process Phase 1 (Pre-melting) Test Results
- Reduction in Carbon Footprint: 20%*
- Pictured: 355MPa grade plates for offshore wind power
- 1)“Low-emission” refers to reduction in CO₂e emissions and should not be interpreted as referring to the reduction of other pollutants or hazardous substances
- 2)Hyundai Steel’s Flat products
- 3)Decision on the adoption of hydrogen-based technology and EAF open based on technological viability and scalability. More information on plans currently under review can be found here.
- 4)20% reduction in carbon emissions refer to CO₂-equivalent (CO₂e) values, calculated internally based on a cradle-to-gate emissions in accordance with international LCA standard ISO 14044, to be verified by third-party in the future.
- 5)Hyundai Steel plans to use hybrid processes, such as the EAF-BF Combined Process to reduce the carbon emission of our products. Although Hydrogen is not currently used in our steelmaking, it symbolizes our company's long-term ambitions of adopting hydrogen-based technologies, which are currently under research and development and require time before commercial scale-up. More information can be found here.
Hyundai Steel’s key carbon neutral technologies
Hyundai Steel’s transition to a carbon neutral system is based on its proprietary carbon neutral technology framework, “Hy-Cube”. The core of the Hy-Cube technology framework is Hy-Arc and hydrogen technology, which, along with CCUS technology that captures inevitably generated carbon, are important technologies for carbon neutrality.
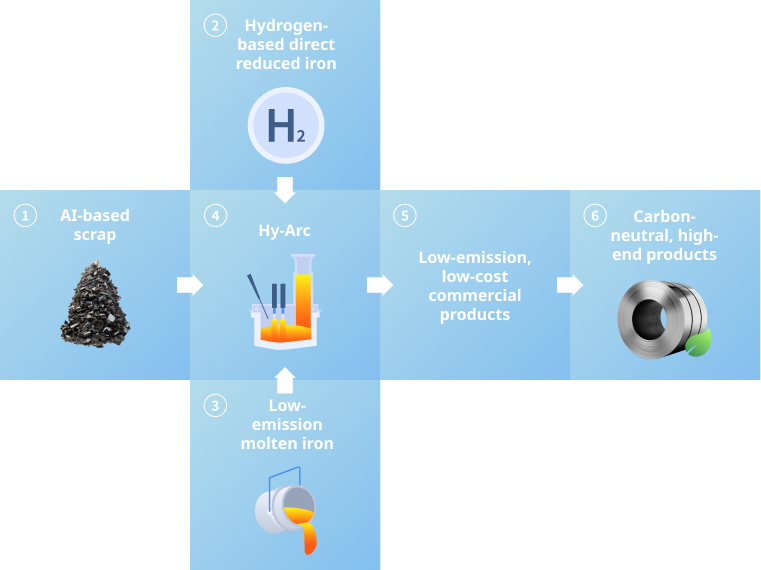
Hy-Cube (Hy3 : Hyundai-Hydrogen-Hybrid)
Hyundai Steel’s long-term goal of achieving carbon neutrality is based in its innovative production system, “Hy-Cube”. Hy-Cube is a technological framework that is centered around the Hy-Arc and hydrogen, and it ensures flexibility across the three core elements of steelmaking: raw materials, processes, and products.
-
- AI-based scrap
- Maximize utilization of lower-grade scrap via AI scrap analysis
-
- Hydrogen-based direct reduced iron
- Increase use of DRI by gradually transitioning towards hydrogen as the primary reducing agent
-
- Low-emission molten iron
- Reduce carbon emission of existing blast furnace process
-
- Hy-Arc
- Operate large-scale electric arc furnace that specializes in rapid melting of hydrogen-based DRI
-
- Low-emission, low-cost commercial products
- Produce low-cost commercial products by using scrap and hydrogen-based DRI
-
- Carbon-neutral, high-end products
- Produce high-quality automotive steel sheets centered around the use of hydrogen-based DRI
- Core facilities of Hy-Cube: Hy-Arc
- Central to Hy-Cube is Hyundai Steel’s proprietary large-scale electric arc furnace, the Hy-Arc, which combines the functions of a blast furnace and a converter. Hy-Arc is the key facility in Hyundai Steel’s carbon-neutral production system, enabling both flexibility and sustainability in steelmaking.
- Key functions of Hy-Arc
-
Performs multiple functions ranging from melting scrap to removing impurities
Able to input various raw materials such as molten steel, hydrogen-based DRI, allowing for flexibility
Hydrogen technology
Upon transitioning to carbon-neutral steelmaking process, it is necessary to transform the conventional coal-based steelmaking to hydrogen-based steelmaking. When transitioned to carbon-neutral steelmaking, hydrogen would be used as a reducing agent, as a fuel for thermal facilities such as preheaters and heating furnaces, and as a source for clean electricity generation. Therefore, producing green hydrogen for the steelmaking is a crucial foundation for achieving carbon neutrality.
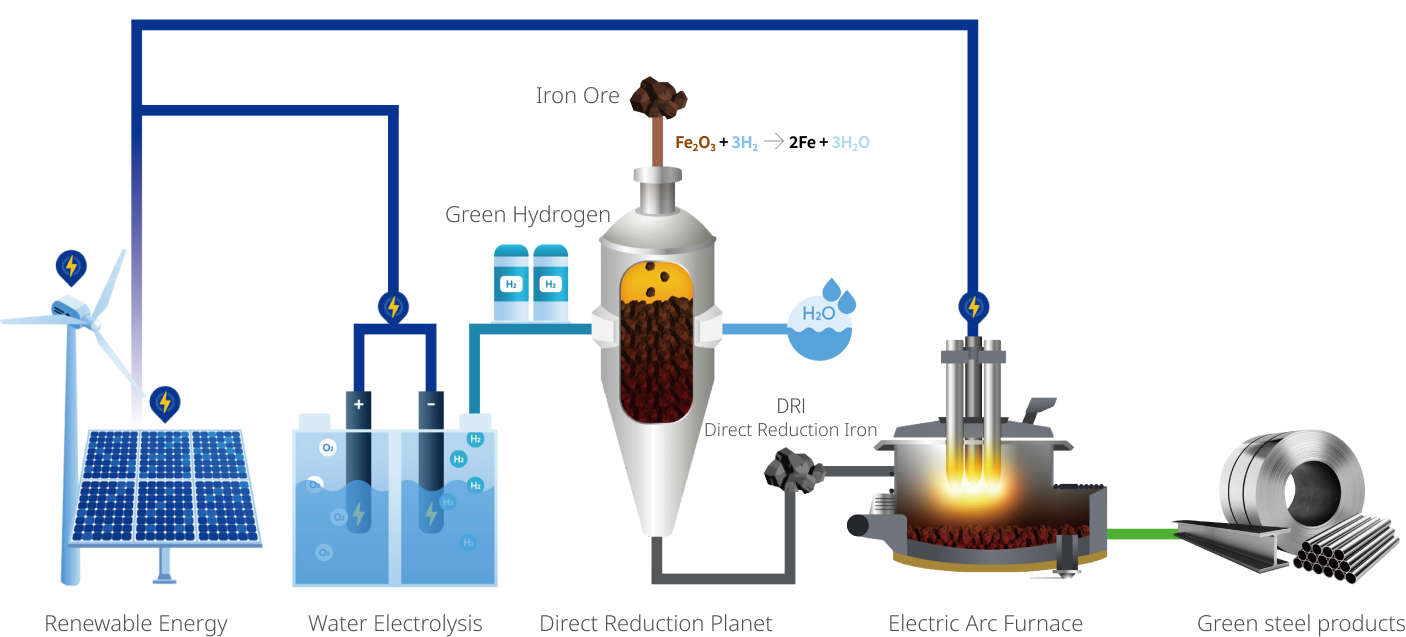
Clean hydrogen production technology

-
- Renewable energy
- Electricity is generated using green energy sources such as wind and solar power
-
- Water electrolysis
- Water electrolysis is a process that uses electricity to separate water into hydrogen and oxygen molecules without emitting any carbon.
-
- Green hydrogen
- Green hydrogen is hydrogen produced using renewable energy sources through the water electrolysis process.
Hydrogen utilization conversion technology
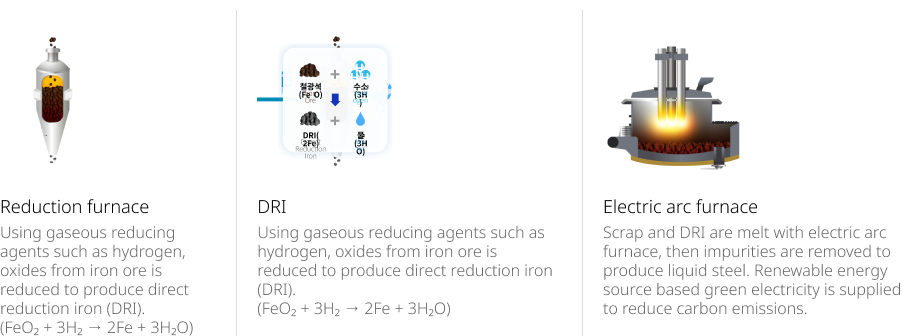
-
- Reduction furnace
- Using gaseous reducing agents such as hydrogen, oxides from iron ore is reduced to produce direct reduction iron (DRI). (FeO2 + 3H2 → 2Fe + 3H2O)
-
- DRI
- Using gaseous reducing agents such as hydrogen, oxides from iron ore is reduced to produce direct reduction iron (DRI). (FeO2 + 3H2 → 2Fe + 3H2O)
-
- Electric arc furnace
- Scrap and DRI are melt with electric arc furnace, then impurities are removed to produce liquid steel. Renewable energy source based green electricity is supplied to reduce carbon emissions.
CCUS technology
In the process of transitioning to carbon-neutral steelmaking processes, some residual carbon emissions may inevitably occur despite various efforts, including hydrogen-based steelmaking. Hyundai Steel plans to manage these residual emissions through CCUS (Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage) technology to achieve carbon neutrality.
What is CCUS technology?
-
- CO2 capture
- Capturing carbon dioxide generated from industrial processes and energy production.
-
- CO2 aggregation and transportation
- Transporting captured CO2 to hubs for storage and utilization.
-
- CO2 storage
- Safely storing remaining CO2 underground to prevent its release into the atmosphere.
-

- CO2 utilization
- Recycling captured CO2 as industrial materials or energy resources.
Necessity of CCUS technology
CCUS technology plays a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions and mitigating global warming by being utilized in various fields such as industrial processes, energy production, and air pollution reduction.
CO2 capture technology
CO2 capture technology is a method for effectively separating and managing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, with the captured CO2 subsequently transported for utilization or underground storage.
 Hyundai Steel’s membrane CO2 capture testing facility
Hyundai Steel’s membrane CO2 capture testing facility
- Liquid solvent CO2 capture process
- CO2 from flue gas is absorbed in liquid-based solvents (e.g., MEA, MDEA). The CO2-rich solvent is then sent to a stripping column, where CO2 is separated and sent for storage or sequestration.
- Dry sorbent CO2 capture process
- CO2 from flue gas is selectively captured by solid sorbents (e.g., zeolites, alkali metal oxides). The CO2 loaded sorbent is then sent to a regeneration unit, where high-purity CO2 is separated and collected for storage or sequestration.
- Membrane CO2 capture process
- Separation of flue gas by selectively allowing CO2 to pass through a porous sheetlike structure with different relative permeation rates. Gases which permeate faster are collected outside of the membrane as permeates, while gases do not permeate so well and stay in side of the membrane are separated out as retentates.
Renewable Energy
With the transition to EAF in mind, Hyundai Steel is preparing for a phased expansion of renewable energy usage. We are reviewing the utilization of a newly completed 11.6MW solar power facility and the installation of an additional 3.2MW facility.
Additionally, in April 2024, HSGA(Hyundai Steel Georgia, Inc.) signed a Virtual Power Purchase Agreement(VPPA) covering approximately 14GWh of annual energy consumption, and we plan to expand renewable energy sourcing to HSAL(Hyundai Steel America, Inc.) as well.



